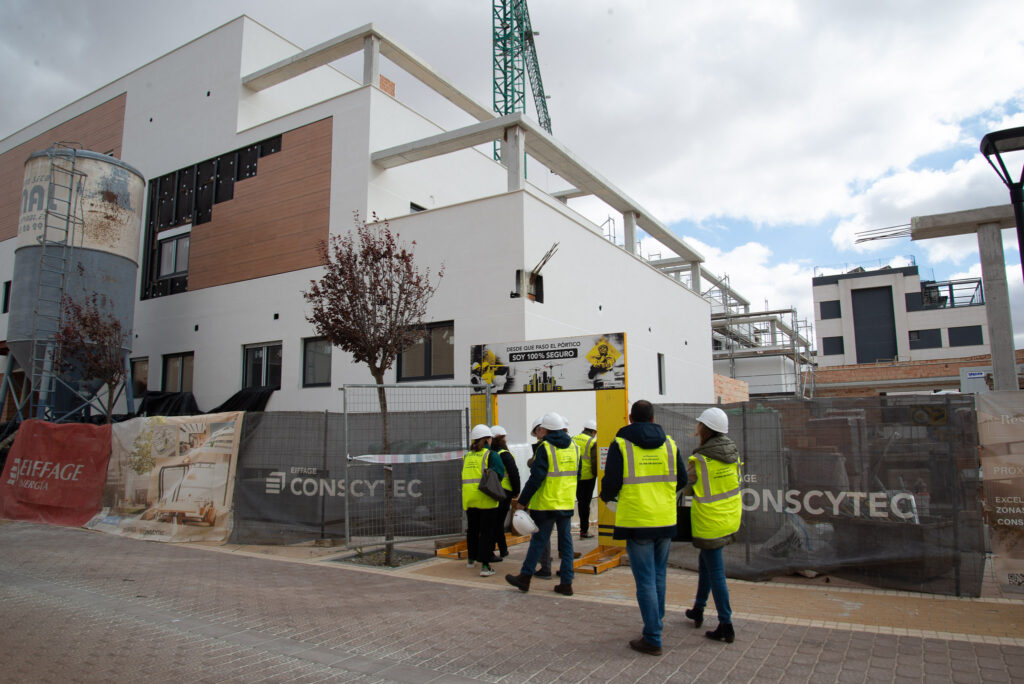
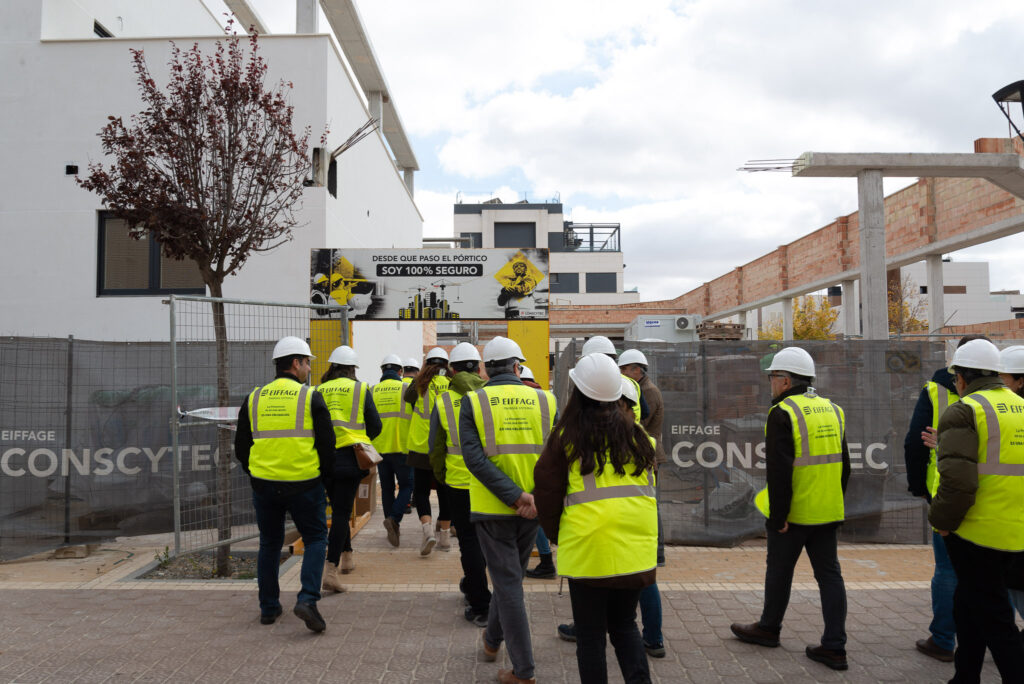
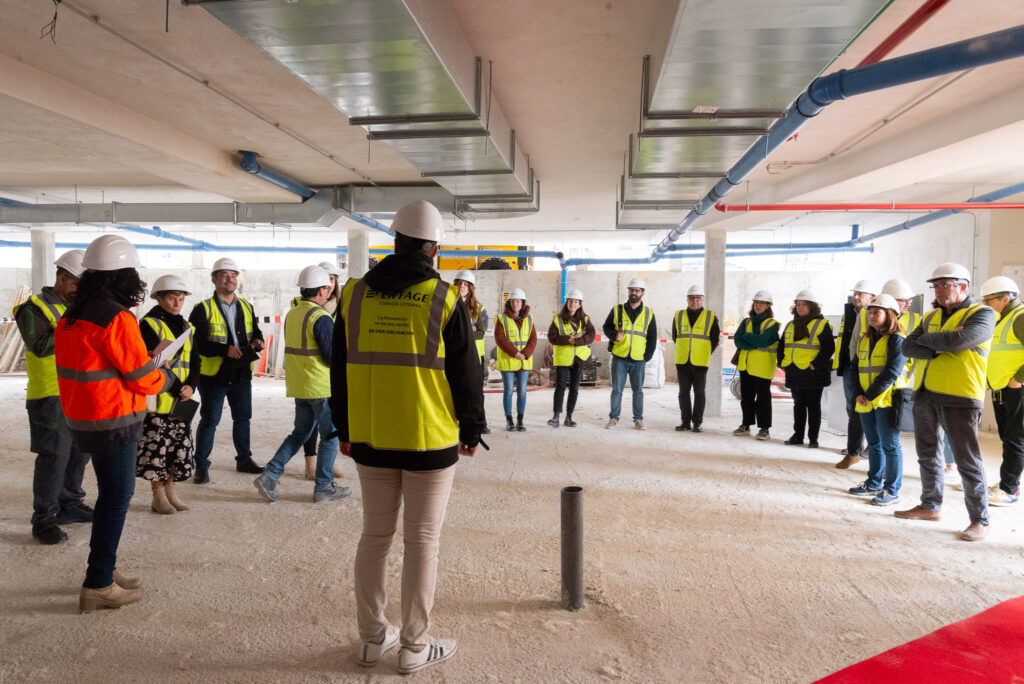
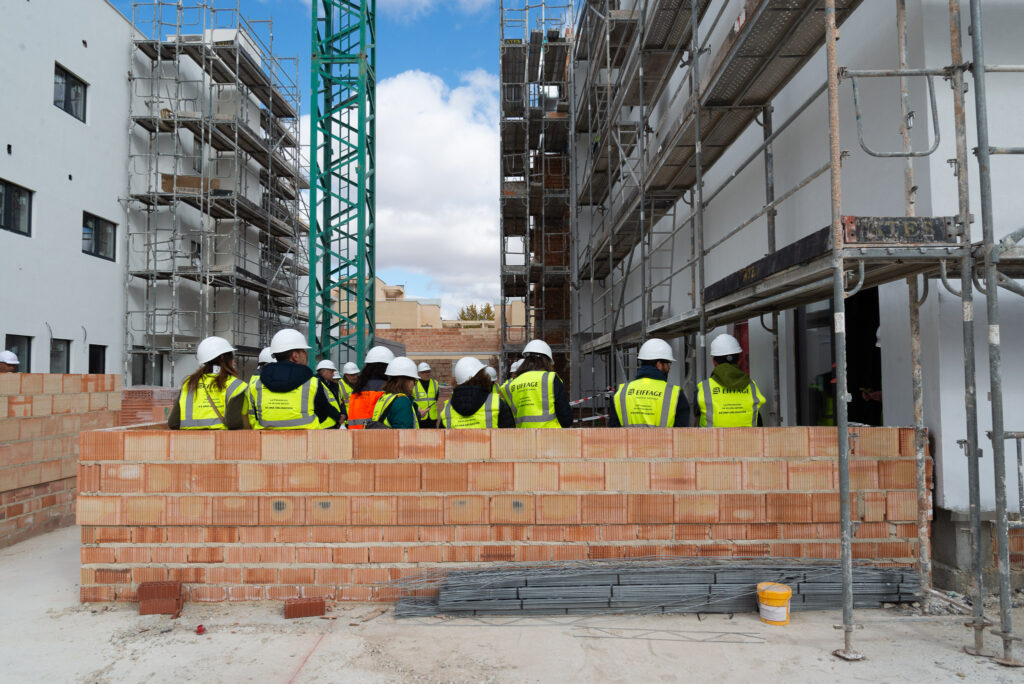
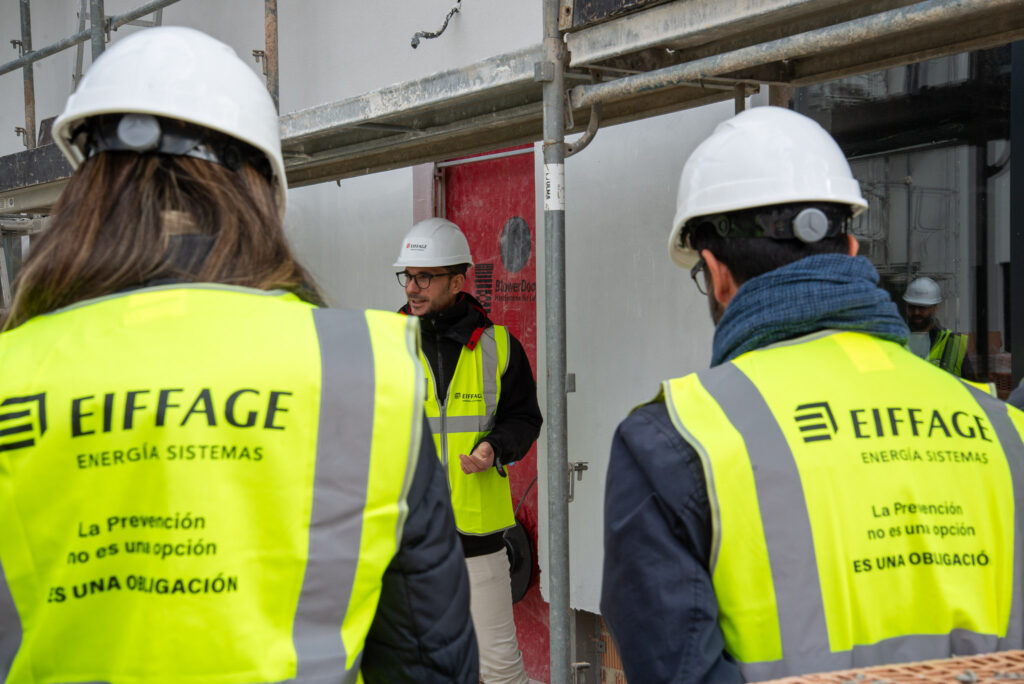
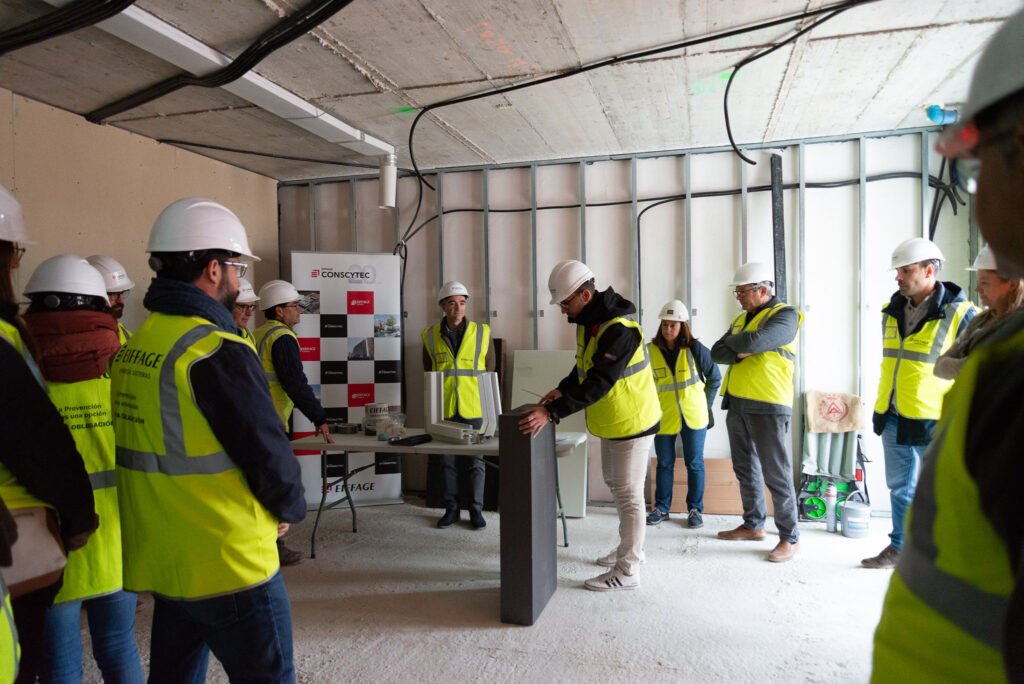
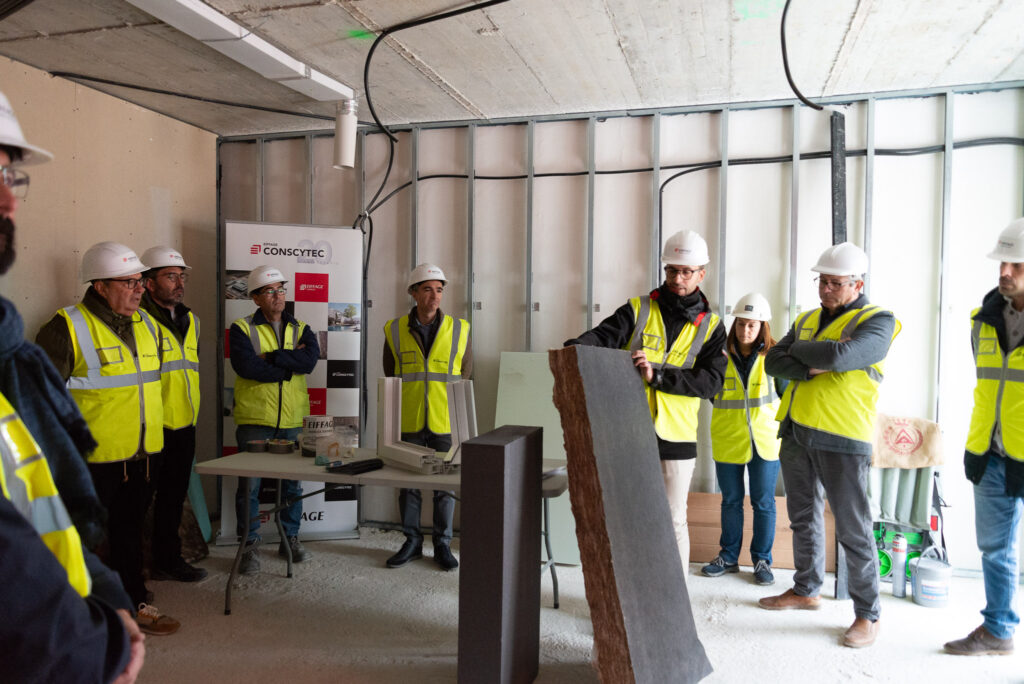
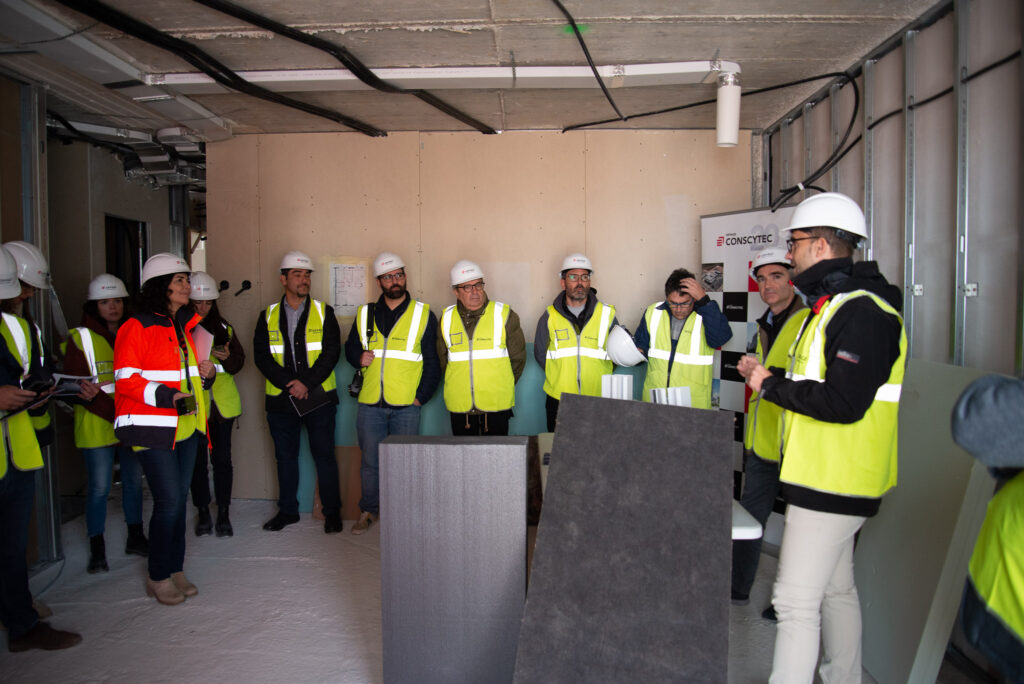
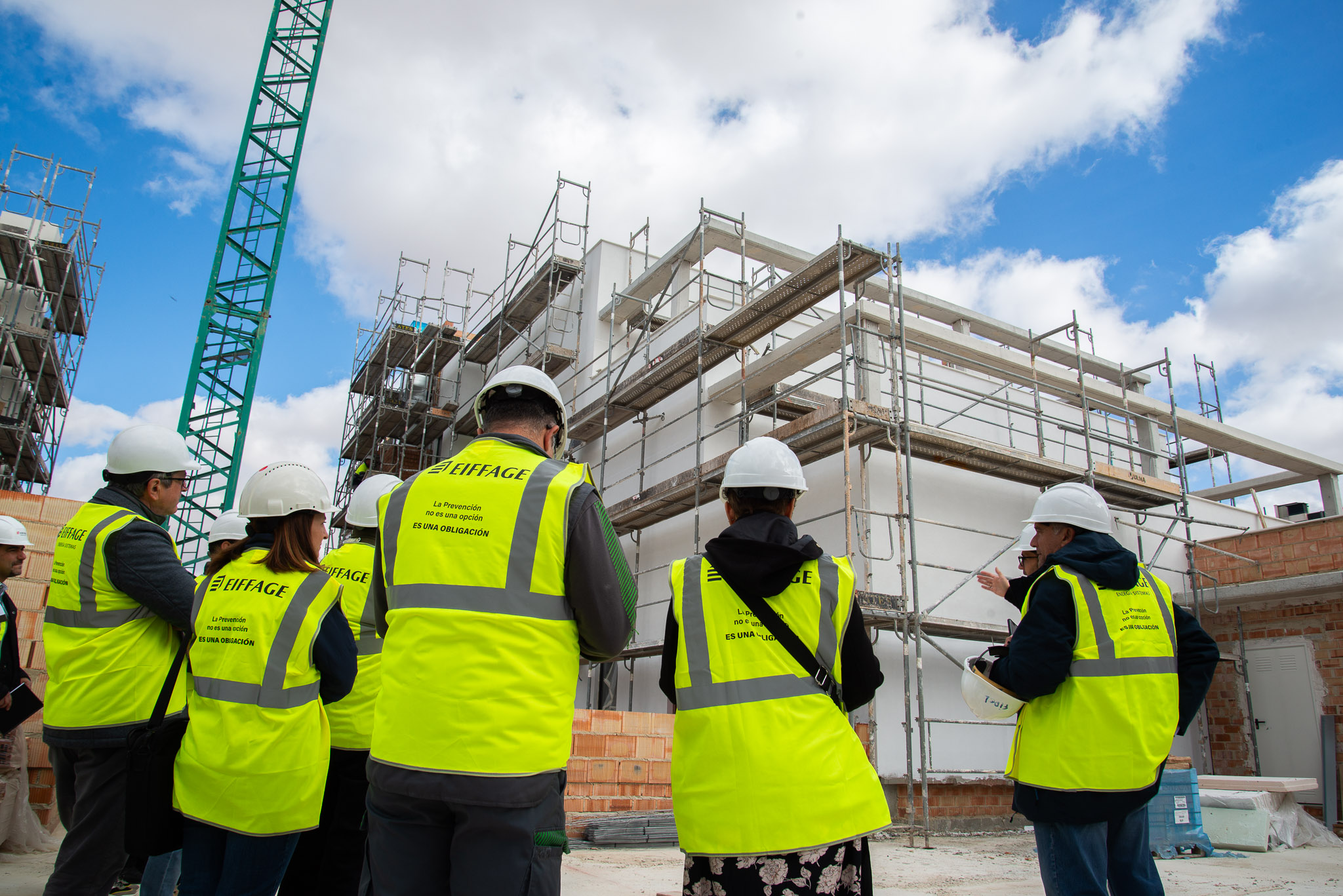
An open day was held last Friday, the 10th of November, organised by the developer Nido Zero at the construction site of the first Passivhaus residential development in Castilla-La Mancha, which is being built by our subsidiary Eiffage Conscytec in Albacete, designed by Relatio and managed by Ingeteo.
It is a building with 18 sustainable homes, located in a residential area next to the Imaginalia shopping centre, and features communal areas such as a swimming pool, gym and children’s play areas.
#iPHopendays
This initiative is part of the 20th anniversary of the International Passivhaus Open Days, IPHA-International Passive House Association – and its affiliates.
The aim is to offer the opportunity to experience first-hand the benefits of the Passivhaus standard and to test the energy efficiency and thermal comfort of buildings that are constructed under the Passivhaus standard guidelines.
This certificate is obtained by meeting a German standard that far exceeds the requirements of the Technical Building Code (TBC). It is a type of construction that uses the resources of bioclimatic architecture. These resources are combined with far better energy efficiency than traditional construction.
Buildings in which heating and cooling requirements are reduced by 75%. Furthermore, the rest of the energy can easily be covered by renewable energies.
The Passivhaus standard
Attendees of the open day had the opportunity to observe the features of this housing type and gain first-hand knowledge about the five fundamental principles of the Passivhaus standard.
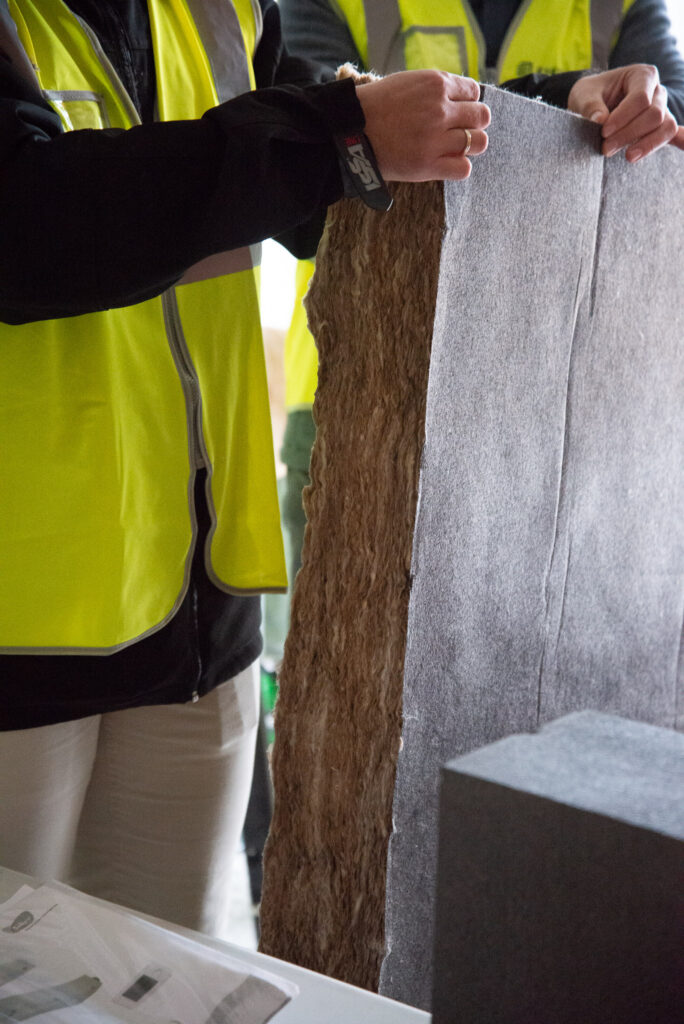
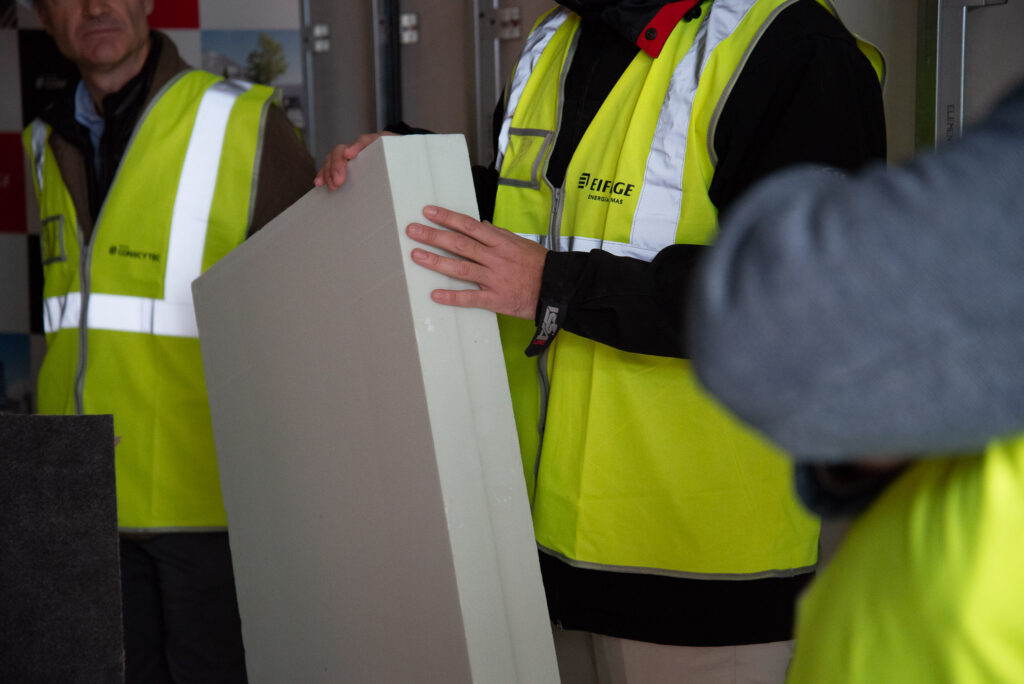
Excellent thermal insulation
Superior insulation of the building envelope offers benefits during both winter and summer. The external walls, roof and floor must have a low thermal transmittance.
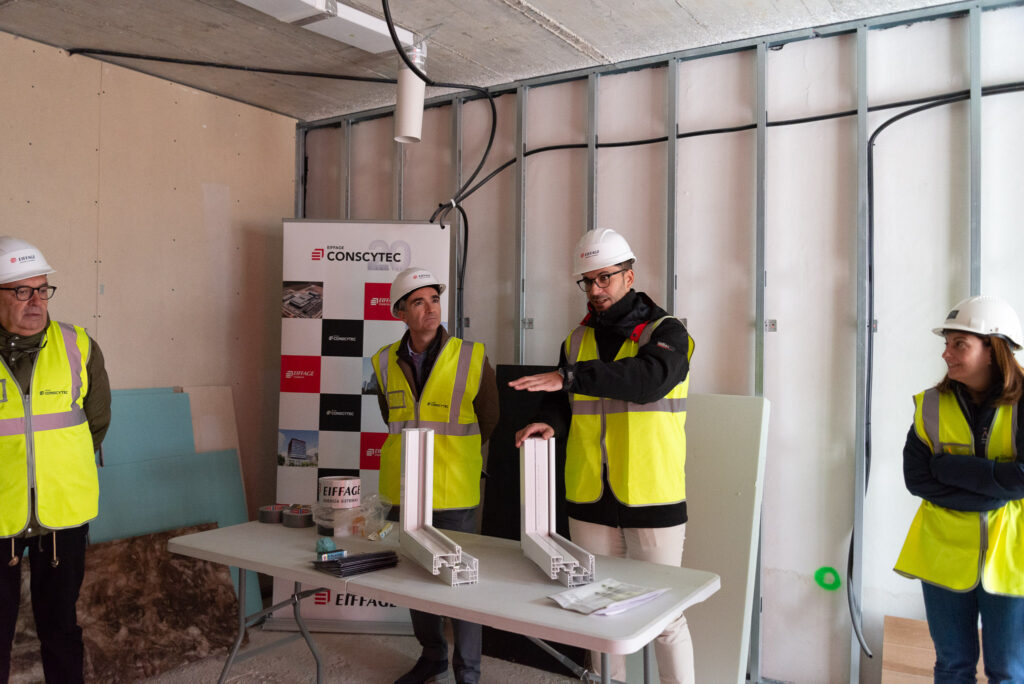
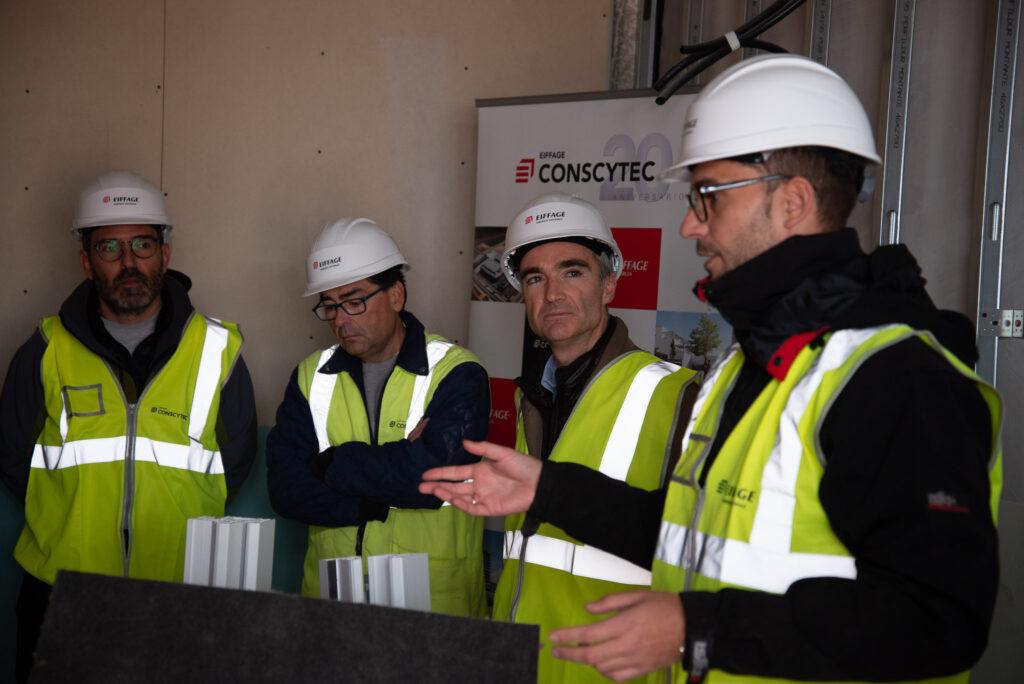
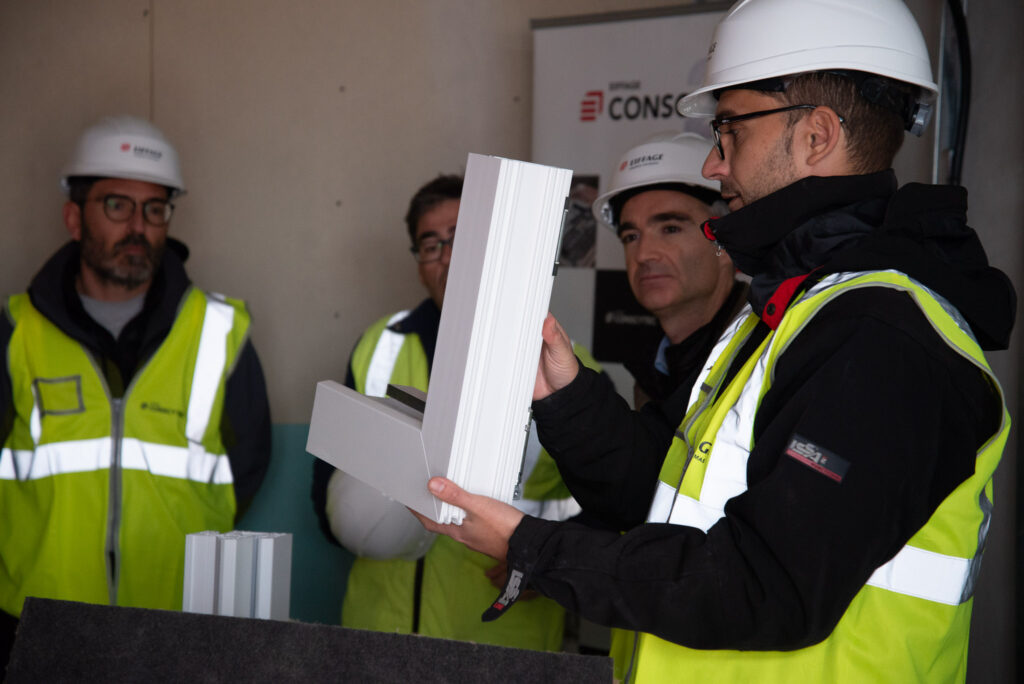
High-performance joinery
Carpentry installed in these buildings features high thermal-acoustic performance. These products have very low thermal transmittance and are constructed with multi-layer glass filled with an inert gas. The glass used is low-emissivity, designed to reflect heat back into the house during winter and keep it out during summer.
Absence of thermal bridges
Unwanted heat losses or gains typically occur at junctions between materials, corners, and joints, where surface temperatures are often lower than the rest of the envelope, potentially leading to mould development and significant energy losses. This issue is mitigated by ensuring continuity in the insulation sheet.
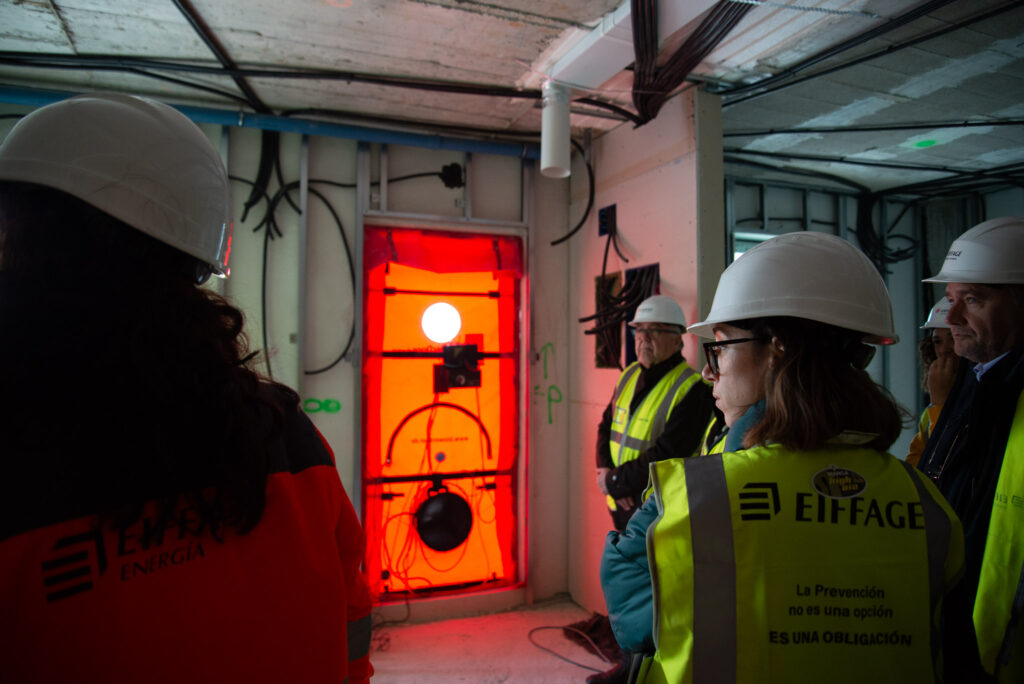
Air tightness
In a Passivhaus building, the envelope is made as airtight as possible to maximize the efficiency of the mechanical ventilation system. This is accomplished by meticulously executing the joints during the construction process.
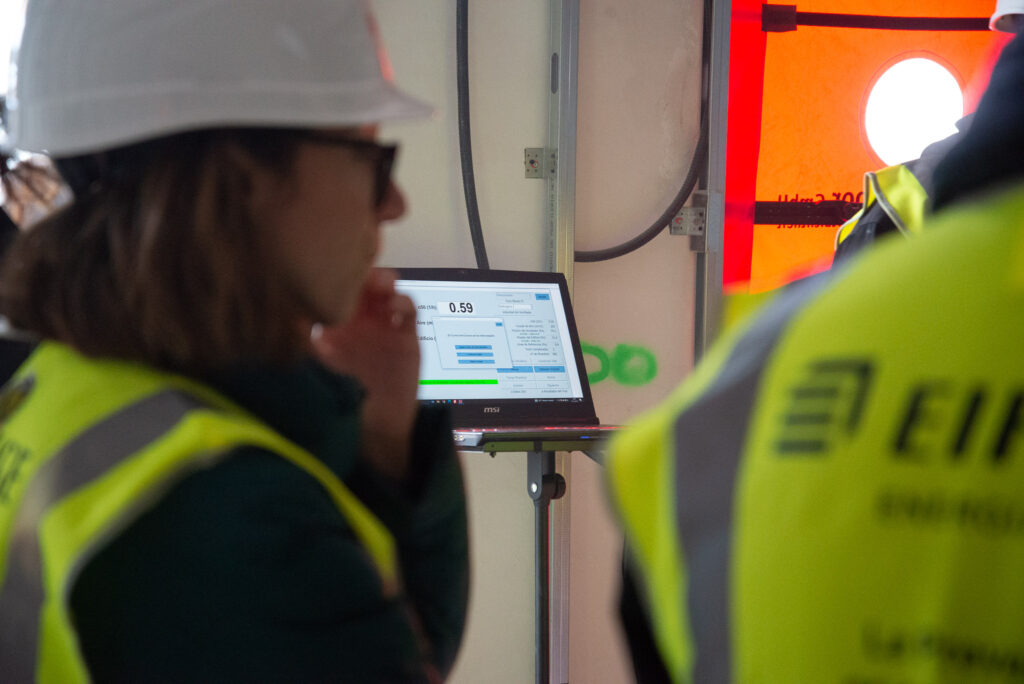
The building’s airtightness is measured using a Blower Door test, which involves creating a pressure difference between the inside and outside using a blower installed at the front door. To comply with the standard, the building must register less than 0.6 air changes per hour at a 50 Pa pressure differential.
Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery
Double-circuit mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery. A device is installed to recover a portion of the conditioned air’s energy inside a room, via the mechanical ventilation system, using an exchanger that facilitates contact between extracted inside air and outside air, while preventing the air in the two circuits from mixing. Ventilation equipment is installed within the building to ensure optimal energy efficiency, high-quality filtering, and a low noise level.
Passivhaus versus TBC
- • Passivhaus is applied uniformly across the entire national territory, irrespective of the building type and its intervention.
- • The TBC, as outlined in the basic documents DB-He and DB-HS, differentiates between new constructions and refurbishments of existing buildings, as well as between residential and other types of uses.
A specific comparison is made between the minimum requirements of these two standards, for this newly constructed building of 18 dwellings in Albacete.
Good execution of the enclosure
In this case, special emphasis is placed on the design and good execution of the enclosure: reinforced thermal insulation; or window frames with triple glazing. The thermal transmittance of façades, roofs and windows is between 30 and 50% lower than TBC 2019.
Thermal bridges are eliminated from the design phase onwards and on-site treatment measures are subject to very strict and documented execution controls.
The airtightness limit value of the building is 0.6 air changes per hour. This is five times lower than the value defined by TBC 2019. This involves careful sealing of joints and openings, as well as a reduction in energy demand by more than 75% compared to a building designed according to TBC 2019.
Dual flow ventilation system
The ventilation system is dual flow and contributes to energy savings through heat recovery. It improves inside air quality thanks to the installation of maximum efficiency filters.
Passivhaus is gaining ground in Spain. Since 2018, European Union member states are under the obligation to ensure that their public buildings are Near-Zero Consumption Buildings. From 2020, this obligation was extended to all new buildings. Hence the importance that is being placed on efficient construction in our country and the rest of Europe.
Every day more and more people choose to live in a house with maximum energy efficiency due to savings, comfort and environmental friendliness.